Prolonged exposure to high fluoride levels during adolescence to adulthood elicits molecular, morphological, and functional impairments in the hippocampus
Por um escritor misterioso
Descrição

Cancer (Molecular) 12 - Oregon Health & Science University

Progesterone activates GPR126 to promote breast cancer development via the Gi pathway
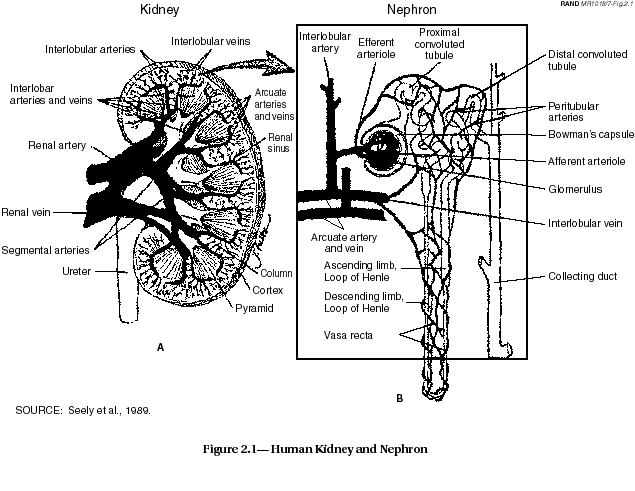
Health Effects

Full article: Fluorine—A current literature review. An NRC and ATSDR based review of safety standards for exposure to fluorine and fluorides

Current Principles of Motor Control, with Special Reference to Vertebrate Locomotion

PDF) Prolonged exposure to high fluoride levels during adolescence to adulthood elicits molecular, morphological, and functional impairments in the hippocampus

Dual Role of the P2X7 Receptor in Dendritic Outgrowth during Physiological and Pathological Brain Development
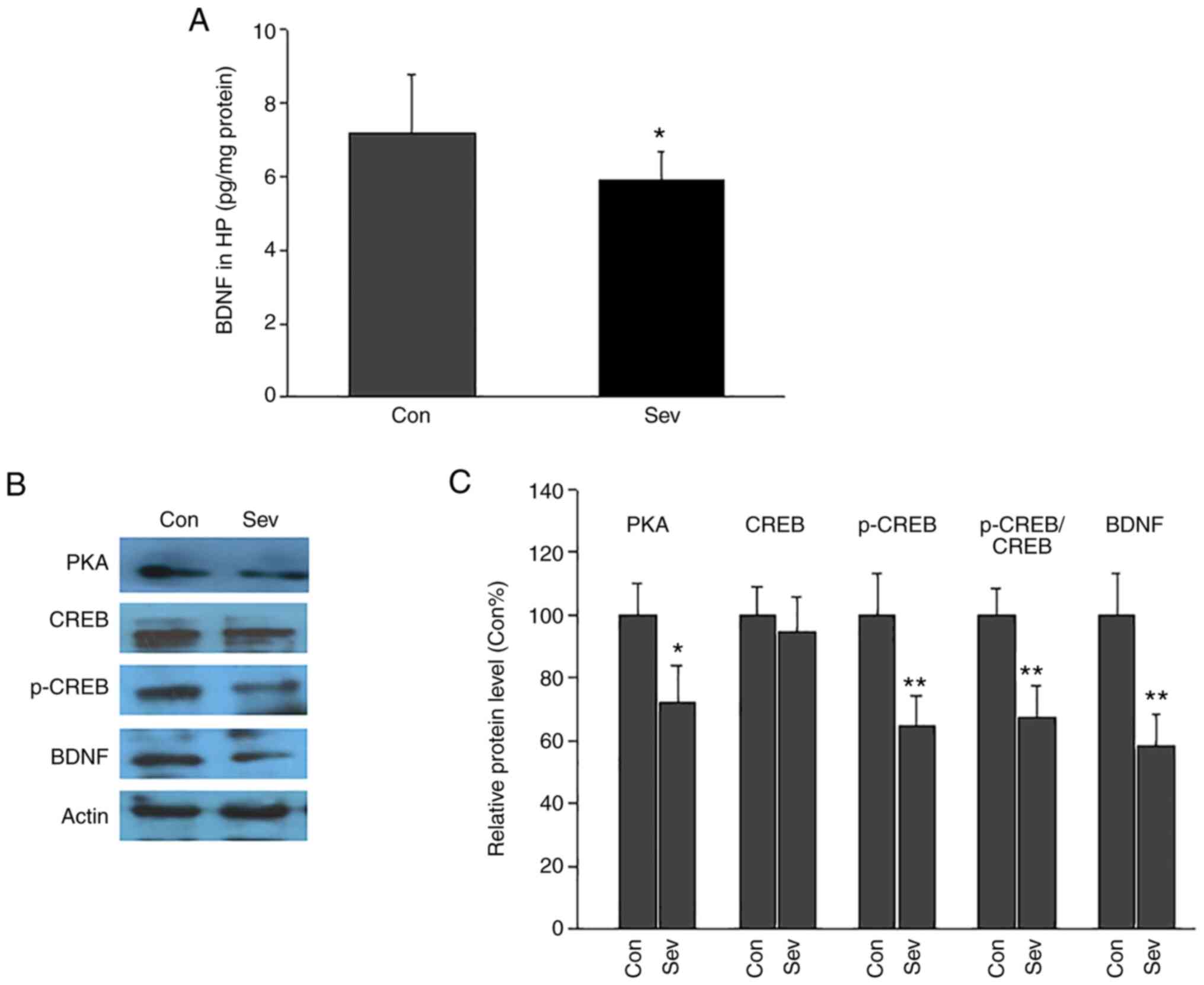
Repeated exposure to sevoflurane in neonatal rats impairs cognition in adulthood via the PKA‑CREB‑BDNF signaling pathway

Frontiers Unraveling molecular characteristic of fluoride neurotoxicity on U87 glial-like cells: insights from transcriptomic and proteomic approach

Fluoride toxicity on central nervous system human cells. Cell viability

Pesticide-Induced Diseases: Learning/Developmental Disorders — Beyond Pesticides

Effects of Perinatal Exposure to Dibutyltin Chloride on Fat and Glucose Metabolism in Mice, and Molecular Mechanisms, in Vitro, Environmental Health Perspectives
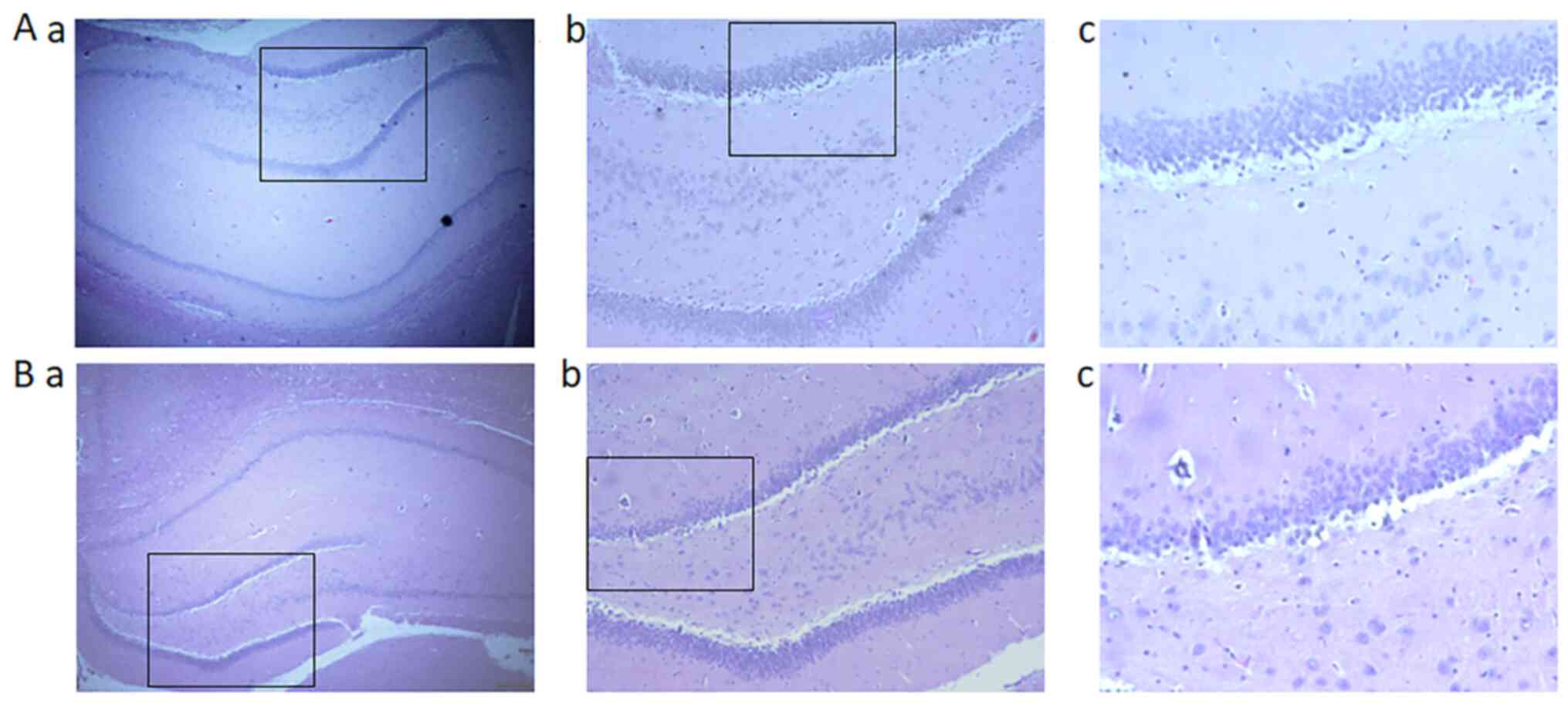
Repeated exposure to sevoflurane in neonatal rats impairs cognition in adulthood via the PKA‑CREB‑BDNF signaling pathway

Fundamental Mechanisms of Regulated Cell Death and Implications for Heart Disease
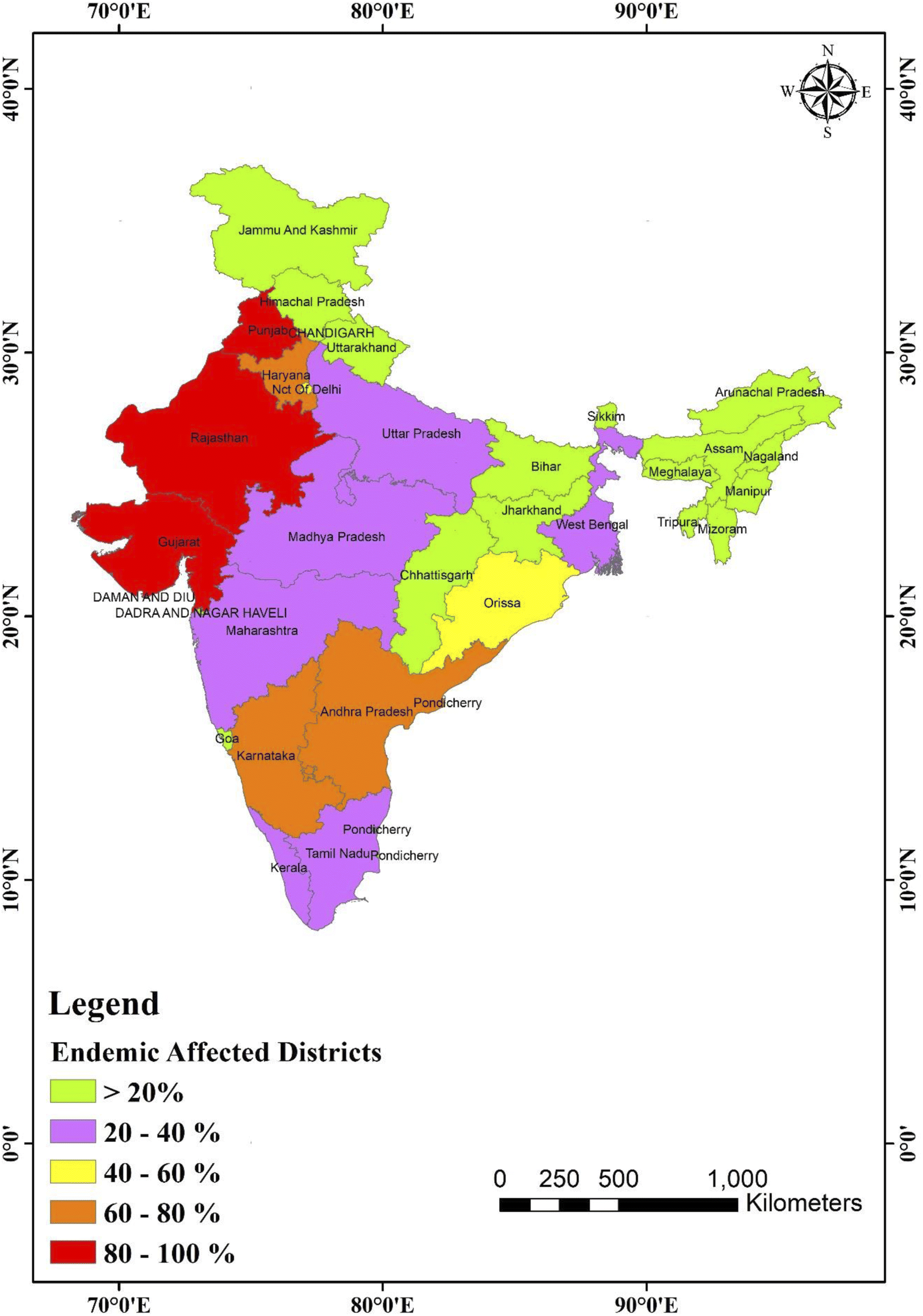
Fluoride contamination, consequences and removal techniques in water: a review - Environmental Science: Advances (RSC Publishing) DOI:10.1039/D1VA00039J
de
por adulto (o preço varia de acordo com o tamanho do grupo)