Labetalol infusion for refractory hypertension causing severe hypotension and bradycardia: an issue of patient safety, Patient Safety in Surgery
Por um escritor misterioso
Descrição
Incremental doses of intravenous labetalol are safe and effective and, at times, such therapy may need to be augmented by a continuous infusion of labetalol to control severe hypertension. Continuous infusions of labetalol may exceed the recommended maximum daily dose of 300 mg on occasion. We report a case in which hypertension occurring after an abdominal aortic aneurysm repair, initially responsive to intermittent intravenous beta-blockade, became resistant to this therapy leading to the choice of an intravenous labetalol infusion as the therapeutic option. The labetalol infusion resulted in a profound cardiovascular compromise in this postoperative critically ill patient. While infusions of labetalol have successfully been used, prolonged administration in the intensive care unit requires vigilance and the establishment of a therapeutic rationale/policy for interventions, such as the ready availability of glucagon, β-agonists, phosphodiesterase inhibitors, insulin, and vasopressin when severe cardiovascular depression occurs.
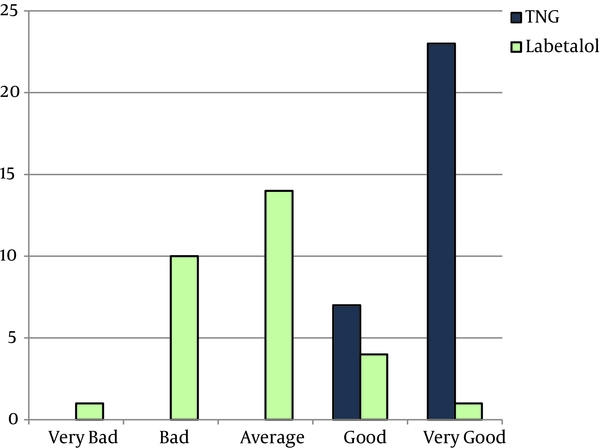
Comparing Labetalol and Nitroglycerine on Inducing Controlled Hypotension and Intraoperative Blood Loss in Rhinoplasty: A Single-Blinded Clinical Trial, Anesthesiology and Pain Medicine

PDF) Labetalol infusion for refractory hypertension causing severe hypotension and bradycardia: An issue of patient safety

Catecholamine-induced hypertensive crises: current insights and management - The Lancet Diabetes & Endocrinology

Management of Women With Acquired Cardiovascular Disease From Pre-Conception Through Pregnancy and Postpartum: JACC Focus Seminar 3/5 - ScienceDirect
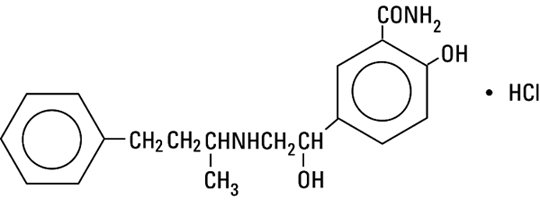
Labetalol: Package Insert

Hypertension Blood Pressure - Cancer Therapy Advisor

Hypertension (Chapter 3) - Post-Anesthesia Care

Acute Hypertension Management in the ICU
PDF) Safety and efficacy of continuous intravenous labetalol for blood pressure control in neurosurgical patients

Hypertension during the Acute Phase of Stroke
LABETALOL HYDROCHLORIDE injection

LABETALOL HYDROCHLORIDE INJECTION, USP 100mg/20mL (5mg/mL) VIAL

Hemodynamic Safety of Continuous Infusion Labetalol Versus Esmolol Combination Therapies for Type B Aortic Dissections

Full article: Remifentanil versus labetalol for deliberate hypotensive anesthesia in children undergoing cochlear implantation: A randomized clinical trial
de
por adulto (o preço varia de acordo com o tamanho do grupo)





/cdn.vox-cdn.com/uploads/chorus_image/image/72057209/RE4_Ganado_Villager_02.0.jpg)

