Diseases, Free Full-Text
Por um escritor misterioso
Descrição
(1) Introduction: Traumatic brain injury (TBI) is a leading cause of injury and mortality worldwide, carrying an estimated cost of $38 billion in the United States alone. Neutrophil to lymphocyte ratio (NLR) has been investigated as a standardized biomarker that can be used to predict outcomes of TBI. The aim of this review was to determine the prognostic utility of NLR among patients admitted for TBI. (2) Methods: A literature search was conducted in PubMed, Scopus, and Web of Science in November 2022 to retrieve articles regarding the use of neutrophil to lymphocyte ratio (NLR) as a prognostic measure in traumatic brain injury (TBI) patients. Inclusion criteria included studies reporting outcomes of TBI patients with associated NLR values. Exclusion criteria were studies reporting only non-primary data, those insufficiently disaggregated to extract NLR data, and non-English or cadaveric studies. The Newcastle-Ottawa Scale was utilized to assess for the presence of bias in included studies. (3) Results: Following the final study selection 19 articles were included for quantitative and qualitative analysis. The average age was 46.25 years. Of the 7750 patients, 73% were male. Average GCS at presentation was 10.51. There was no significant difference in the NLR between surgical vs. non-surgical cohorts (SMD 2.41 95% CI −1.82 to 6.63, p = 0.264). There was no significant difference in the NLR between bleeding vs. non-bleeding cohorts (SMD 4.84 95% CI −0.26 to 9.93, p = 0.0627). There was a significant increase in the NLR between favorable vs. non-favorable cohorts (SMD 1.31 95% CI 0.33 to 2.29, p = 0.0090). (4) Conclusions: Our study found that NLR was only significantly predictive for adverse outcomes in TBI patients and not surgical treatment or intracranial hemorrhage, making it nonetheless an affordable alternative for physicians to assess patient prognosis.

Eradication of Diseases - Our World in Data
AI for Research

RePub, Erasmus University Repository: The rise and fall of diseases: reflections on the history of population health in Europe since ca. 1700

Eradication of Diseases - Our World in Data

Global, regional, and national incidence, prevalence, and years lived with disability for 310 diseases and injuries, 1990–2015: a systematic analysis for the Global Burden of Disease Study 2015 - The Lancet

Free radicals and polyphenols: The redox chemistry of neurodegenerative diseases - ScienceDirect

Infectious Diseases

Autophagy in the Pathogenesis of Disease: Cell

Spring cure. Doctor Quenaudon's extract of green herbs for purifying the blood and the cure of all diseases arising from its impurity, also of all other chronic diseases Dr. D. V.

Global Burden of Cardiovascular Diseases and Risk Factors, 1990–2019: Update From the GBD 2019 Study - ScienceDirect

A randomized-controlled trial of ischemia-free liver transplantation for end-stage liver disease - ScienceDirect

Mandell, Douglas, and Bennett's Principles and Practice of Infectious Diseases: Expert Consult Premium Edition - Enhanced Online Features and Print (Two Volume Set): Gerald L. Mandell: 9780443068393: : Books
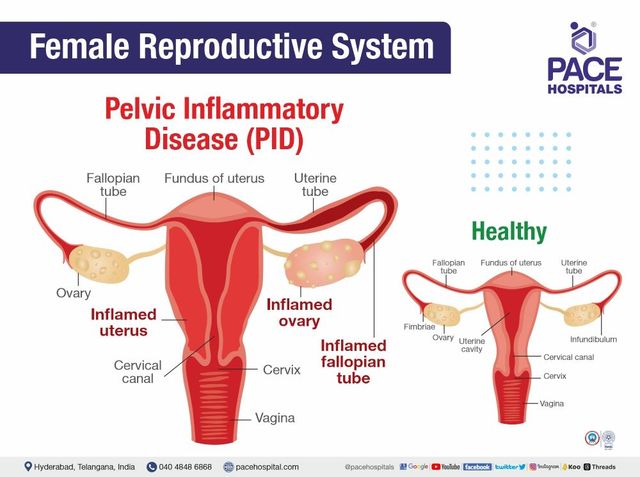
Pelvic Inflammatory Disease (PID) Symptoms, Causes, Risk Factors
de
por adulto (o preço varia de acordo com o tamanho do grupo)







