Cells, Free Full-Text
Por um escritor misterioso
Descrição
The enteric nervous system (ENS) constitutes the largest part of the peripheral nervous system. In recent years, ENS development and its neurogenetic capacity in homeostasis and allostasishave gained increasing attention. Developmentally, the neural precursors of the ENS are mainly derived from vagal and sacral neural crest cell portions. Furthermore, Schwann cell precursors, as well as endodermal pancreatic progenitors, participate in ENS formation. Neural precursors enherite three subpopulations: a bipotent neuron-glia, a neuronal-fated and a glial-fated subpopulation. Typically, enteric neural precursors migrate along the entire bowel to the anal end, chemoattracted by glial cell-derived neurotrophic factor (GDNF) and endothelin 3 (EDN3) molecules. During migration, a fraction undergoes differentiation into neurons and glial cells. Differentiation is regulated by bone morphogenetic proteins (BMP), Hedgehog and Notch signalling. The fully formed adult ENS may react to injury and damage with neurogenesis and gliogenesis. Nevertheless, the origin of differentiating cells is currently under debate. Putative candidates are an embryonic-like enteric neural progenitor population, Schwann cell precursors and transdifferentiating glial cells. These cells can be isolated and propagated in culture as adult ENS progenitors and may be used for cell transplantation therapies for treating enteric aganglionosis in Chagas and Hirschsprung’s diseases.

Advancing synthetic biology through cell-free protein synthesis - ScienceDirect
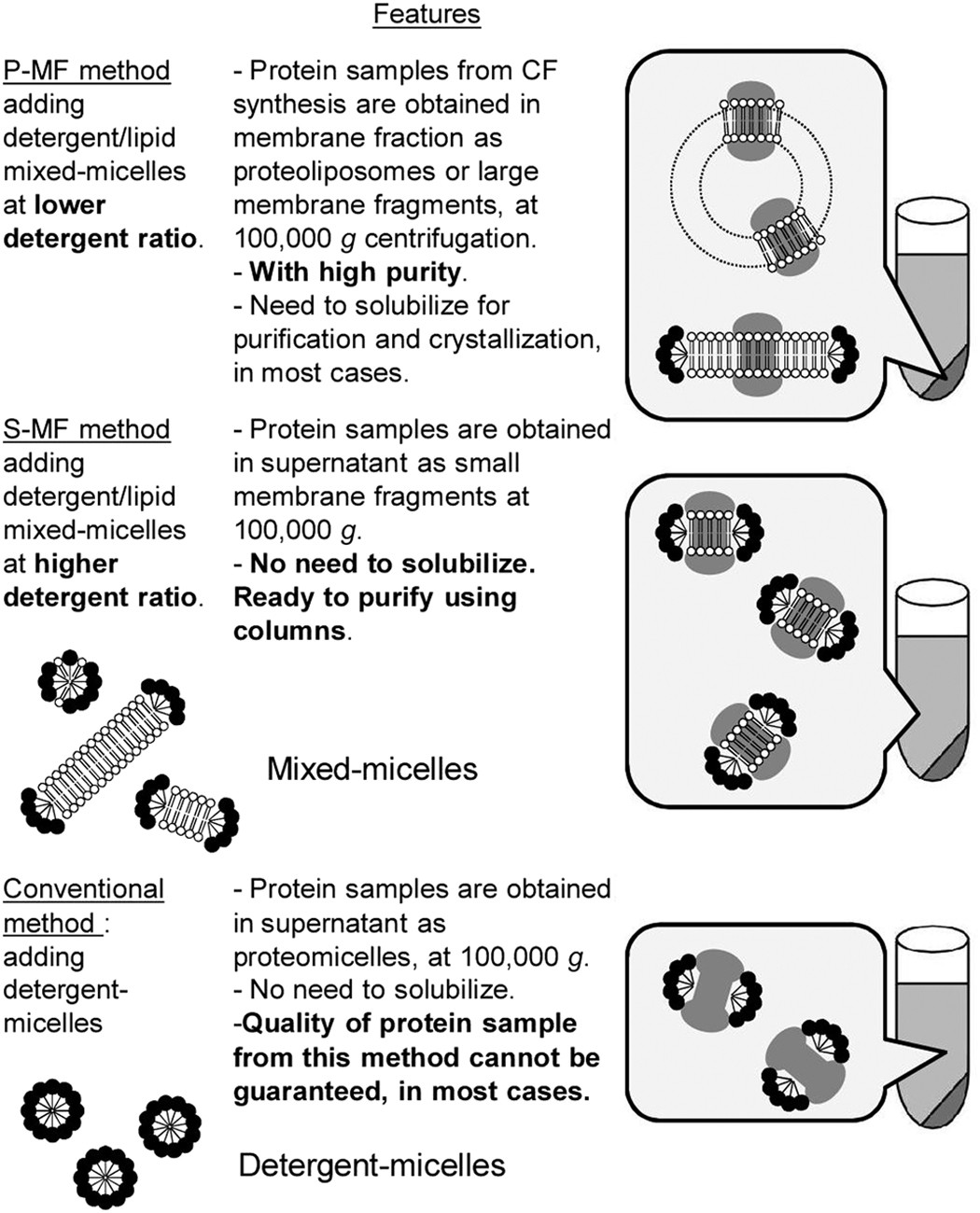
Cell-free methods to produce structurally intact mammalian membrane proteins
Cells, Free Full-Text

Cell-free expression and synthesis of viruses and bacteriophages: applications to medicine and nanotechnology - ScienceDirect
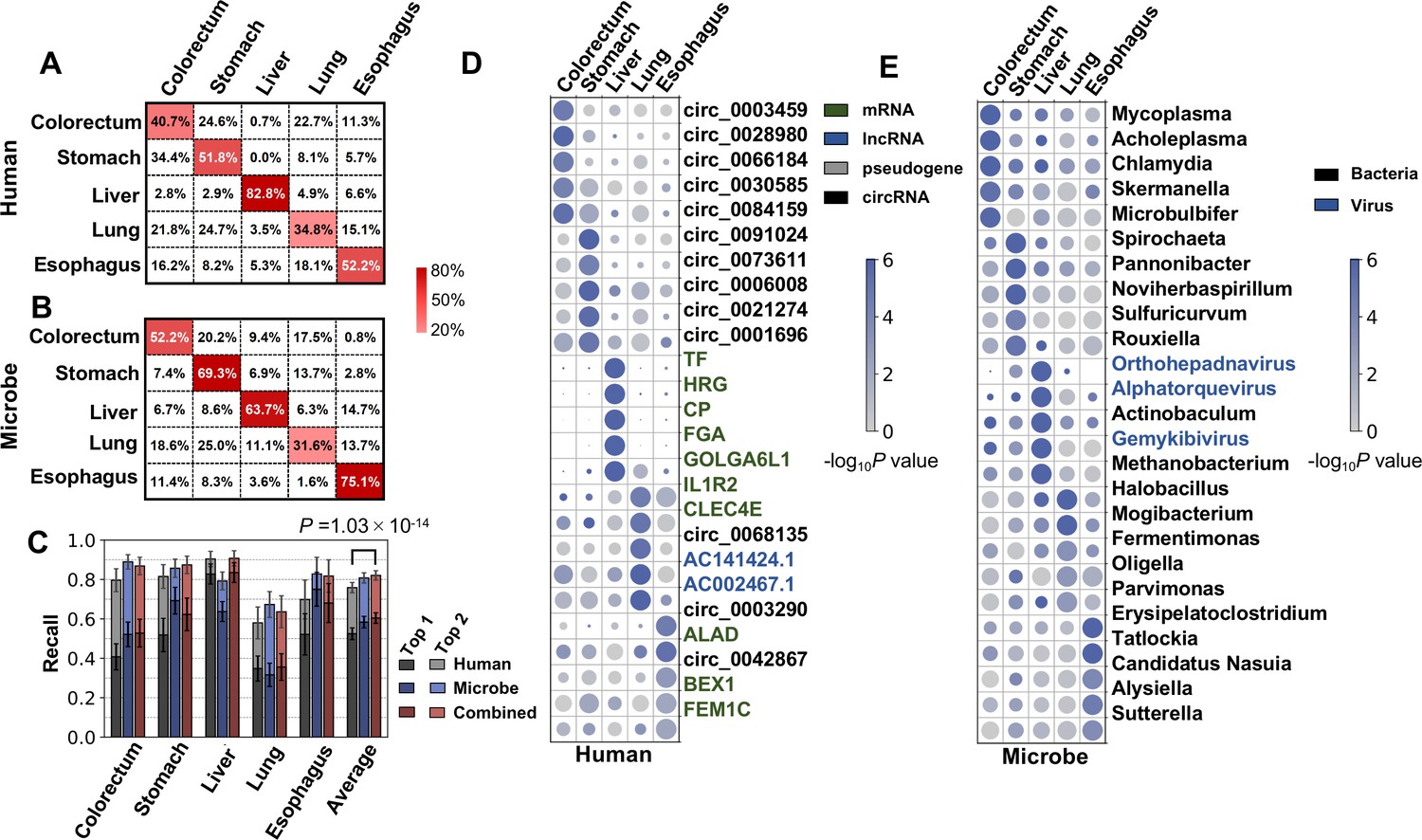
Cancer type classification using plasma cell-free RNAs derived from human and microbes
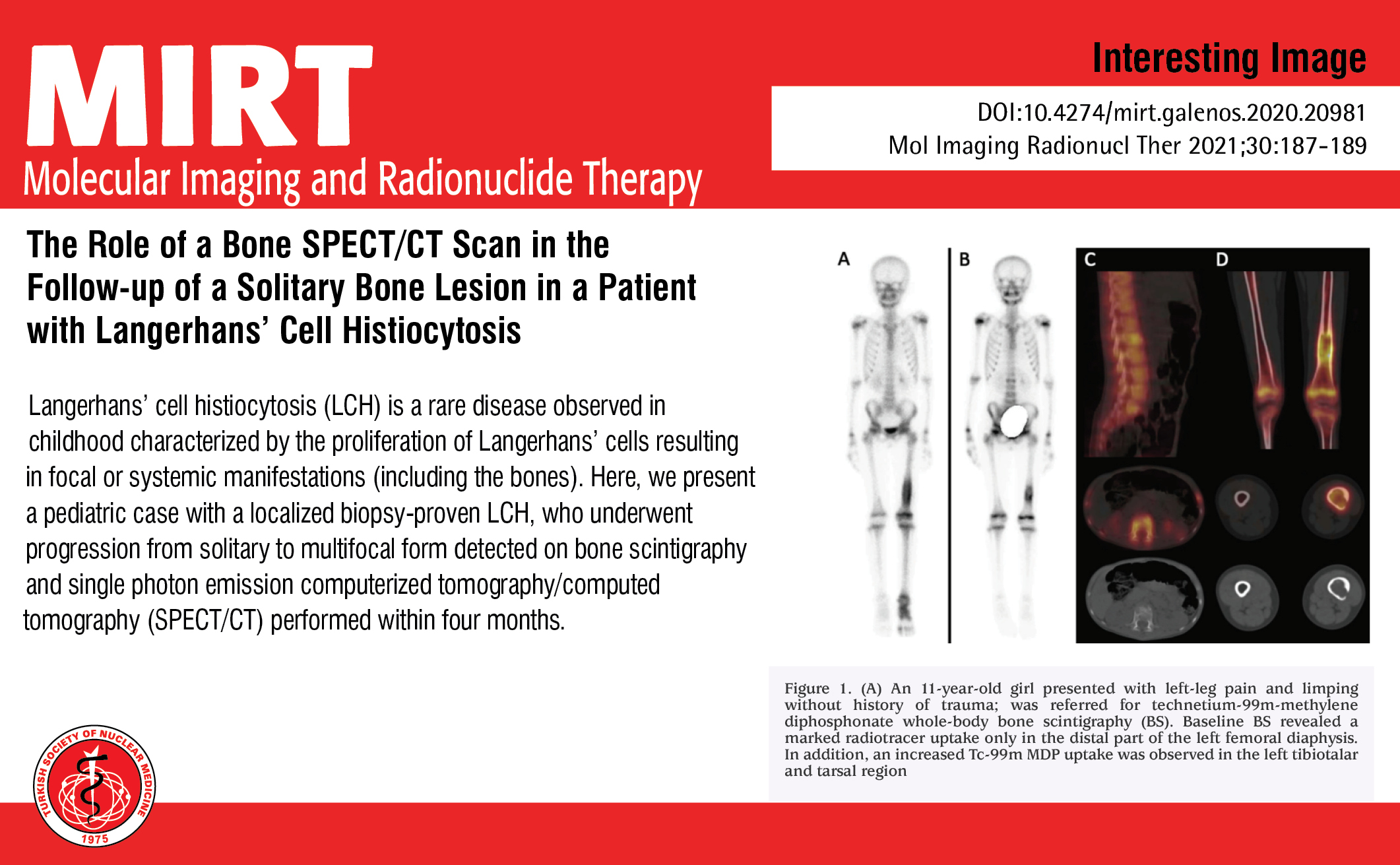
Mol Imaging Radionucl Ther on X: The Role of a Bone SPECT/CT Scan in the Follow-up of a Solitary Bone Lesion in a Patient with Langerhans' Cell Histiocytosis You can see the

Sequencing of Circulating Cell-free DNA during Pregnancy
THE LIVES OF A CELL : LEWIS THOMAS : Free Download, Borrow, and Streaming : Internet Archive
Labile coat: reason for noninfectious cell-free varicella-zoster virus in culture. - Abstract - Europe PMC

Harnessing Extracellular Vesicles for Regenerative Therapy - Gowing Life

Towards reproducible cell-free systems

A) Cell-free expression of sfGFP fused to a variety of N-and
de
por adulto (o preço varia de acordo com o tamanho do grupo)







