Biomedicines, Free Full-Text
Por um escritor misterioso
Descrição
Infections are important factors contributing to the morbidity and mortality among elderly patients. High rates of consumption of antimicrobial agents by the elderly may result in increased risk of toxic reactions, deteriorating functions of various organs and systems and leading to the prolongation of hospital stay, admission to the intensive care unit, disability, and lethal outcome. Both safety and efficacy of antibiotics are determined by the values of their plasma concentrations, widely affected by physiologic and pathologic age-related changes specific for the elderly population. Drug absorption, distribution, metabolism, and excretion are altered in different extents depending on functional and morphological changes in the cardiovascular system, gastrointestinal tract, liver, and kidneys. Water and fat content, skeletal muscle mass, nutritional status, use of concomitant drugs are other determinants of pharmacokinetics changes observed in the elderly. The choice of a proper dosing regimen is essential to provide effective and safe antibiotic therapy in terms of attainment of certain pharmacodynamic targets. The objective of this review is to perform a structure of evidence on the age-related changes contributing to the alteration of pharmacokinetic parameters in the elderly.

Systemic Perturbations in Amine and Kynurenine Metabolism Associated with Acute SARS-CoV-2 Infection and Inflammatory Cytokine Responses

Collaboration with Generate Biomedicines
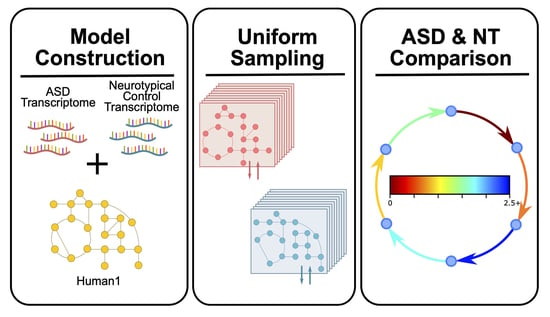
Crack Asd 2014 Get File - Colaboratory
Biomedicines
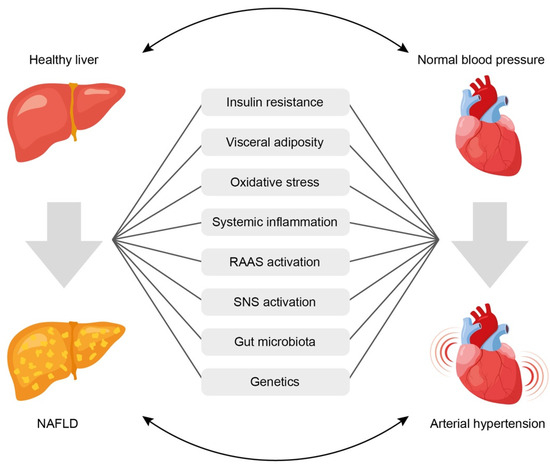
License Key File Scavenger Version 4.1 - Colaboratory

The effect of probiotics on immune responses and their therapeutic application: A new treatment option for multiple sclerosis - ScienceDirect
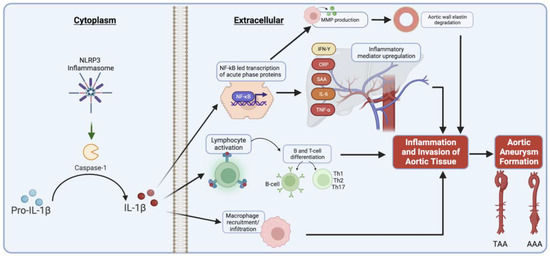
Biomedicines An Open Access Journal from MDPI
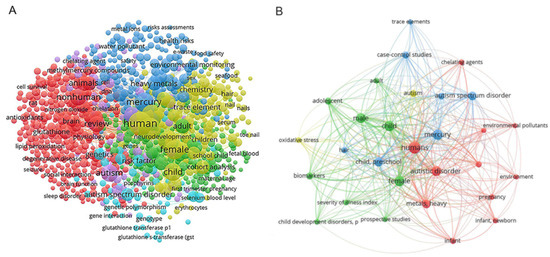
Biomedicines An Open Access Journal from MDPI

Full article: In silico screening of phytopolyphenolics for the identification of bioactive compounds as novel protease inhibitors effective against SARS-CoV-2
de
por adulto (o preço varia de acordo com o tamanho do grupo)







